How to set up a MariaDB Database with Docker Compose
If you’re looking to create a simple blog or website, having a reliable database management system is crucial. In this guide, we’ll walk you through setting up a MariaDB database using Docker Compose, and we’ll even throw in phpMyAdmin for easy database management.
Getting Started
Before we dive in, make sure you have Docker and Docker Compose installed on your system. These tools will allow us to easily manage and deploy our database and web applications.
Docker Compose Configuration
Let’s start by creating a docker-compose.yml file in your project directory. This file will contain the configuration for both MariaDB and phpMyAdmin services.
version: '3.8'
services:
mariadb:
image: mariadb:latest
container_name: my-mariadb-container
restart: always
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: your_root_password
MYSQL_DATABASE: your_database_name
MYSQL_USER: your_database_user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: your_database_password
volumes:
- ./data:/var/lib/mysql
ports:
- "3306:3306"
phpmyadmin:
image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin:latest
container_name: my-phpmyadmin-container
restart: always
environment:
PMA_HOST: mariadb
PMA_PORT: 3306
ports:
- "8080:80"
depends_on:
- mariadb
Change the image line to specify the desired version of MariaDB. For example, if you want to use version 10.6.5, replace latest it with 10.6.5 as shown above.
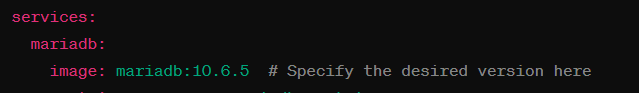
By specifying a version number in this way, Docker Compose will pull and use that specific version of the MariaDB image instead of the latest one. This can be useful for ensuring consistency and compatibility with your application requirements.
MariaDB Service
We define a mariadb service using the latest MariaDB image from Docker Hub. This service will create a MariaDB container with the specified environment variables for the root password, database name, user, and password. We also mount a volume to persist the database data.
phpMyAdmin Service
The phpmyadmin service uses the phpMyAdmin image and sets up environment variables to connect to the MariaDB service. We expose a port 8080 on the host to access phpMyAdmin via the web browser.
Running the Services
To start the services, navigate to the directory containing the docker-compose.yml file and run:
docker compose up -d
If you want to watch the log files just skip the -d param at the end:
docker compose up
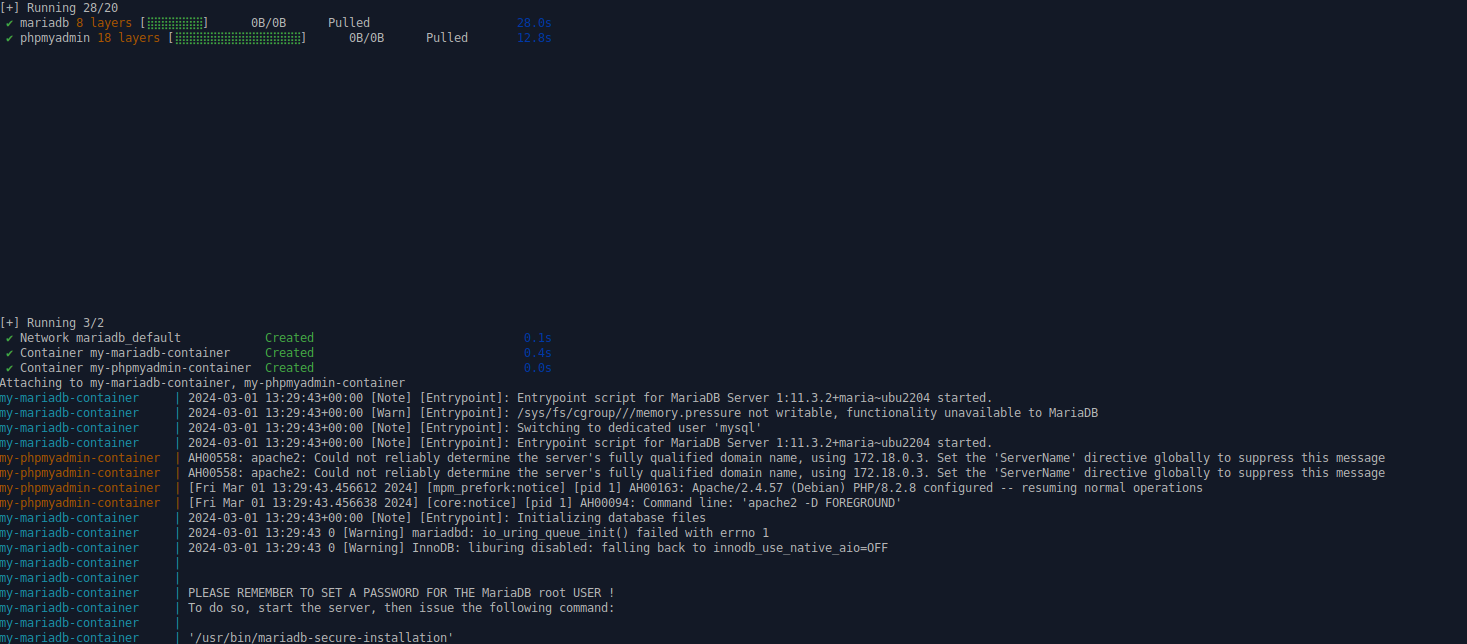
Both MariaDB and phpMyAdmin containers will start up, allowing you to manage your database easily.
Accessing phpMyAdmin
Open your web browser and navigate to http://localhost:8080. You’ll be greeted with the phpMyAdmin login page, where you can log in using the credentials specified in the docker-compose.yml file.
Views: 68
